
Guanxi in Chinese business is one of the most important concepts a foreign executive can understand. If you spend enough time operating in China, you’ll realize something essential: deals don’t move because of contracts — they move because of relationships.
This relationship system has a name: guanxi (关系), and it influences every partnership, negotiation, and long-term decision.
Guanxi is not about favoritism, nor is it bribery, nor simply “who you know.”
It’s a structured system of trust, obligation, and mutual benefit — one that has governed Chinese society for thousands of years.
If you don’t understand the role of guanxi in Chinese business, your JV decisions, supplier choices, or internal management will consistently surprise you. This article will help you see what your Chinese counterparts already know.
1. What Guanxi Actually Is (And Isn’t)
Many Westerners interpret guanxi as:
- “connections”
- “networking”
- “pulling strings”
- or even corruption
But guanxi is something very different.
Guanxi = a long-term, reciprocal relationship built through repeated trust.
It includes:
- mutual obligations
- shared history and favors
- personal credibility
- ongoing exchanges of support
- a sense of moral responsibility
If you’ve read my article on Common Mistakes Foreign Leaders Make in China, this aligns with a core theme: China evaluates trust before capability.
Harvard Business Review reinforces this cultural truth:
“Top leaders build trust across cultures through mindset, character, shared experience, and results.”
Source: HBR How Leaders Build Trust
Guanxi is closer to family-like loyalty than normal corporate networking.
You don’t network your way into guanxi — you earn your way into it.
In Western business culture, trust grows after clear expectations.
In China, especially when navigating guanxi in Chinese business, clear expectations grow after trust.
2. Why Guanxi Matters So Much in Chinese Business
Chinese business culture relies on a foundational belief:
People are more reliable than systems.
Contracts can be interpreted.
Regulations can change.
Policies vary across provinces, cities, or even individual districts.
But a person with strong guanxi in Chinese business?
- returns your call
- solves problems quietly
- speaks well of you in rooms you are not in
- warns you early when something shifts
- sticks with you even in difficult periods
This loyalty explains why two suppliers with identical pricing can perform very differently.
It’s why a JV board either resolves conflict smoothly — or becomes gridlocked.
It’s why one government bureau accelerates approvals while another delays them.
McKinsey reinforces this:
“As China’s economy evolves, relationships and trust networks increasingly determine how foreign companies succeed.”
Source: McKinsey: Inside dynamics of a changing relationship
It also connects directly to concepts in The Hidden Power of Face in Chinese Business Culture, because face (mianzi) and guanxi operate together to preserve trust and respect.
The Economist adds that privately run Chinese companies succeed not just through policy or capital, but through deeply rooted networks and long-term relationships.
Source: The Economist: Private Cos. Roots in China
3. The Three Circles of Guanxi in Chinese Business
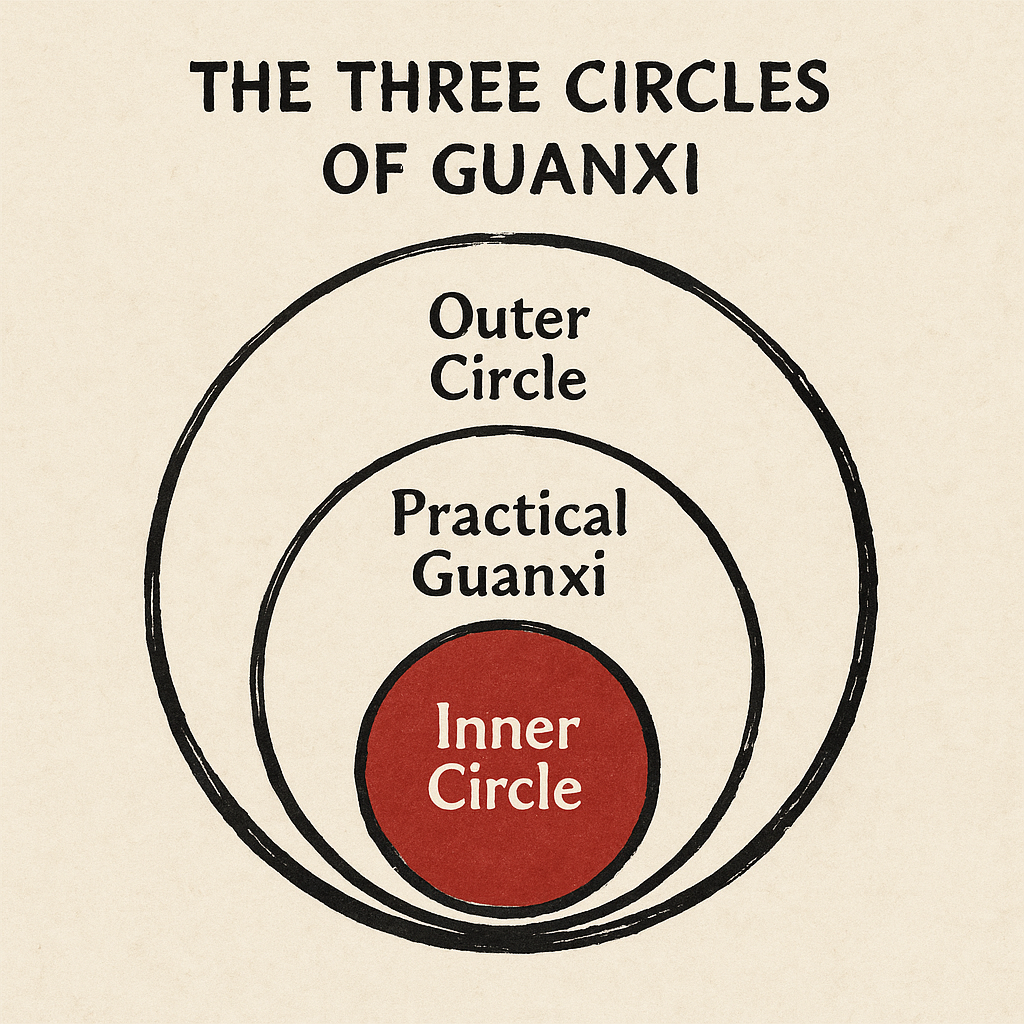
Guanxi networks are layered, and where you sit determines how decisions flow.
Level 1: The Inner Circle (Core Guanxi)
Family, long-term friends, and individuals with decades of shared history.
Carries:
- highest obligation
- fastest action
- strongest loyalty
Most foreign executives never enter this level — and don’t need to.
Most success involving guanxi in Chinese business happens in Level 2.
Level 2: Practical Guanxi (Working Trust)
This is where productive collaboration happens.
Repeated cooperation creates:
- mutual reliability
- personal rapport
- direct problem-solving
This is where Chinese partners begin treating you as “one of us.”
Level 3: Transactional Relationships (Outer Circle)
No history.
Low trust.
Short-term cooperation only.
This is where most Western executives mistakenly assume they’re operating — but Chinese partners may see it as an early-stage relationship not yet ready for trust.
Your effectiveness in China depends heavily on which of these circles you occupy.
4. Guanxi Is Built, Not Bought
You cannot buy guanxi with gifts, dinners, or referrals.
Those things are symbols, not substance.
Real guanxi grows from:
- Consistency — you do what you say
- Reliability — you solve problems
- Respect — you avoid public embarrassment
- Reciprocity — you return favors
- Loyalty — you show long-term commitment
- Discretion — you protect private conversations
This is why:
- Long-term partners remain even at slightly higher cost
- JV decisions favor relationship stability
- Chinese suppliers prefer private issue resolution
- Leaders ask “Do we trust them?” before “Do they have capability?”
Within guanxi in Chinese business, the progression is:
Trust → Long-term performance → Formal agreements
not the Western sequence:
Agreements → Performance → Trust
5. How Guanxi Shapes Business Behavior Westerners Misread
A. “Why do they go straight to the CEO?”
Because the CEO is the highest guanxi holder.
B. “Why didn’t we get early warning?”
You aren’t in the information circle.
C. “Why was our proposal rejected with no explanation?”
The relationship foundation wasn’t ready.
D. “Why are they so indirect with feedback?”
They are protecting your face — essential for maintaining guanxi.
Understanding guanxi in Chinese business eliminates misinterpretation and frustration. This is also important in building trust with Chinese partners.
6. How Foreign Leaders Can Build Guanxi (The Right Way)
The blueprint:
✔ Show long-term commitment
Partners must know you’re invested — not transactional.
✔ Spend time outside formal meetings
Meals, conversation, travel — not PowerPoints — build trust.
✔ Always return favors
Big or small. Reciprocity is oxygen for guanxi.
✔ Protect face (mianzi)
Public embarrassment destroys guanxi instantly.
✔ Be reliable when it matters most
Crisis moments deepen trust faster than years of normal operations.
✔ Be patient
Strong guanxi grows slowly — and becomes incredibly durable.
Understanding guanxi in Chinese business helps foreign leaders interpret decisions and timeline shifts more accurately.
7. Why Guanxi Matters Even More in Joint Ventures
Foreign–domestic JVs are among the most guanxi-dependent business structures in China.
Inside a JV:
- decisions often happen informally
- influence flows through personal channels
- trust determines speed
- disagreements are resolved privately long before the meeting
Foreign–domestic JVs are among the most guanxi-dependent business structures in China.
When guanxi in Chinese business is strong:
- decisions accelerate
- conflict disappears
- partners protect each other externally
- the JV becomes more stable than either shareholder alone
When guanxi is weak:
- decisions become political
- approvals slow
- misunderstandings multiply
- alignment fractures
This dynamic is closely tied to decision making in China, where alignment often forms privately before anything is discussed in a formal meeting.
In a JV, guanxi is not a soft skill.
It is the operating system.
8. Final Thought: Guanxi Isn’t a Strategy — It’s a Relationship Philosophy
Guanxi is not a tactic.
It is a relationship philosophy rooted in:
- genuineness
- consistency
- reciprocity
- trust
- mutual respect
If you treat guanxi as manipulation, people feel it instantly.
If you treat it as partnership, they open the circle.
In China, relationships are strategy.
And guanxi in Chinese business is how those relationships endure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Before you go, here are some common questions executives ask about Guanxi—and why it remains one of the most misunderstood foundations of Chinese business culture.
1. What does Guanxi actually mean in Chinese business?
Guanxi refers to the network of trusted relationships that guide cooperation, decision-making, and long-term support in Chinese business. It is built on mutual respect, reliability, and shared history—not quick transactions or favors.
2. Why is Guanxi so important in Chinese companies?
Guanxi reduces risk in environments where contracts, processes, or institutions may not be fully trusted. Strong relationships create smoother negotiations, faster approvals, and more predictable cooperation. For Chinese partners, trust often matters just as much as commercial terms.
3. How do you build Guanxi with Chinese business partners?
Guanxi develops through consistent behavior over time: showing reliability, spending time together outside formal meetings, respecting hierarchy, and supporting partners when it is inconvenient. Small gestures and shared experiences matter more than formal statements.
4. How is Guanxi different from Western networking?
Western networking focuses on exchanging information or opportunities. Guanxi is deeper and more personal—closer to a long-term social obligation. Once a relationship is established, both sides are expected to help each other without immediately calculating benefit.
5. Can Guanxi replace contracts or formal agreements?
No. Guanxi complements contracts but does not replace them. Formal agreements provide structure, while relationships determine how smoothly those agreements function in practice. The most successful foreign companies in China combine both.
Enjoying this?
Get weekly, real-world insights on China joint ventures and China manufacturing.
